Norfloxacin: Uses And Side Effects
Norfloxacin is a bactericidal antibiotic that is used against bacterial infectious diseases. Find out about the use and side effects of this drug.

Norfloxacin is an antibiotic that belongs to the group of quinolones. It has a broad-spectrum bactericidal effect against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic pathogenic microorganisms.
This antibiotic inhibits the bacterial synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. Due to its strong bactericidal effect, it is used against microorganisms that are resistant to other drugs.
What is norfloxacin used for?
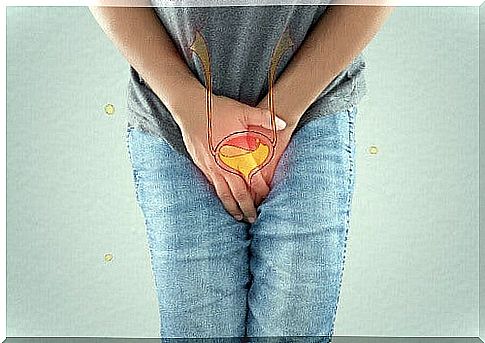
Norfloxacin belongs to the pharmacotherapeutic group of urinary tract antiseptics and anti-infectives. It is used to treat the following urinary tract infections:
- Cystitis: complicated acute inflammation of the urinary bladder
- Recurring chronic urinary tract infections
- Cystopyelitis: inflammation of the urinary bladder and renal pelvis
It is best to do a culture to analyze the susceptibility of the microorganism that is causing the infection to be treated.
How to take norfloxacin
First of all , this drug must be taken outside of meals, that is, an hour before or two hours after meals. The form of administration depends on the outcome of the culture and the severity of the disease.
For adults with urinary tract infections , take 1 tablet every 12 hours for 7 to 10 days. However, the duration of treatment is shortened to 3 to 7 days for uncomplicated acute cystitis.
In the case of recurring chronic infections, it can be extended up to 12 weeks. However, if you get a good result after 4 weeks, you can reduce the dose to once a day.
Side effects of norfloxacin
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal, psychological and skin reactions. However , nausea, headache, dizziness, heartburn, pain, and diarrhea can also occur.
It can however also occur other less common side effects, but serious longer-lasting and may be irreversible in some cases.
These can negatively affect the organism and trigger various disorders and reactions.
Hypersensitivity reactions and gastrointestinal disorders
They include:
- Anaphylaxis
- Angioedema
- Dyspnea
- Vasculitis
- Urticaria
- arthritis
- Myalgia and arthralgia
Also gastrointestinal diseases such as pseudomembranous colitis, and in rare cases, pancreatitis, hepatitis and jaundice may subsequently arise.

Skin and subcutaneous tissue
There have been cases of photosensitivity reactions in patients treated with norfloxacin who have been exposed to the sun for long periods of time.
If you experience these symptoms, you must stop treatment. Also, avoid direct sunlight during treatment to avoid possible risks of photosensitivity. The following reactions can also occur:
- Exfoliative dermatitis
- Erythema multiforme
- Vasculitis
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Steven Johnson Syndrome
Skeletal muscle and connective tissue
Tendon inflammation or a torn tendon, especially the Achilles tendon, can also result. A crack can appear on both sides.
Cases of this condition have occurred within 48 hours of treatment with quinolones and fluoroquinolones. Some have even been seen for up to several months after stopping treatment.
The risk of tendonitis and a tendon rupture is increased in the following cases:
- Advanced age
- Patients who have received a solid organ transplant
- Kidney failure
- Patients being treated concomitantly with corticosteroids
At the first signs of tendonitis, such as pain or inflammation , treatment with norfloxacin should be discontinued and alternative treatment should be considered. On the other hand, the affected part of the body must be cared for accordingly so that it can properly recover.
Peripheral neuropathy
There were reported cases of sensitive polyneuropathy or motor-sensory polyneuropathy. This condition can lead to paraesthesia, hypoaesthesia, dysesthesia, or weakness.
Patients treated with norfloxacin should tell their doctor if symptoms of neuropathy occur. These symptoms include tingling, burning, pain, numbness, or weakness.
In this way it is possible to prevent the development of possible irreversible diseases.
heart
In some cases, quinolone drugs have been associated with QT prolongation on electrocardiograms. But only in very rare cases has it been associated with arrhythmias.
For this reason , caution should be exercised in patients with hypokalaemia and significant bradycardia. Care must also be taken with patients treated with class Ia or III antiarrhythmics.
conclusion
According to the AEMPS (Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products), quinolones or fluoroquinolones should only be used in exceptional cases to treat mild or moderate infections. That is, when other antibiotics are not effective or are not tolerated by the patient.
Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about treatment with this drug. This way you will avoid complications.