Prebiotics And Probiotics: What’s The Difference?
Today we explain the difference between prebiotics and probiotics, which complement each other. Find out more about this topic and also which foods you can find prebiotics and probiotics in.
Prebiotics and probiotics are very beneficial for health. The difference lies fundamentally in their function and in which foods they can be found. Today we are going into more detail on this topic because there is often confusion.
Billions of microorganisms colonize our intestines: The microbiota, also known as the intestinal flora or microbiome, forms an important part of our immune system.
All of these gut bacteria can be classified into two types: the healthy microorganisms that we need and the harmful ones that need to be kept in check. The latter can cause diarrhea, infections or flatulence, for example.
On the other hand, the beneficial intestinal bacteria help us to keep the harmful ones under control. The microbiota is also fundamental to our immune system, reduces gas formation and improves digestion. In addition, it is necessary to synthesize various vitamins and to be able to absorb certain nutrients.
Our health and our state of mind depend, among other things, on our microbiota, which should always be healthy and balanced. But what do prebiotics and probiotics have to do with it? Find out more about it afterwards.
The main difference between prebiotics and probiotics
There are two basic things to keep the intestinal flora in a balanced state:
- To supply the organism with probiotics in order to constantly absorb healthy living microorganisms.
- Take prebiotics to nourish the healthy intestinal bacteria well.
So you can already see where the main difference between prebiotics and probiotics lies. In addition, there are of course other differences that we will explain in more detail.
Prebiotics, or the food of our microbiota
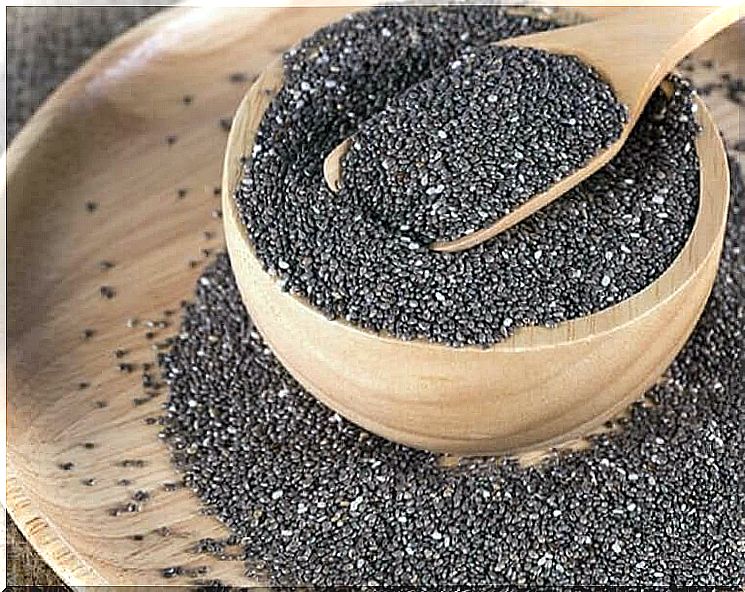

Prebiotics are indigestible food ingredients that nourish healthy gut bacteria, which have enzymes to break them down.
Prebiotics therefore promote the growth and activity of these healthy intestinal bacteria, which improves the health of the host (our health). The following criteria must be met to be considered a prebiotic:
- The food ingredients must be indigestible in the stomach and small intestine, so they are not absorbed.
- They have to be fermented by the intestinal bacteria as soon as they arrive in the colon.
- This fermentation must promote the activity and proliferation of certain intestinal bacteria that have beneficial effects on the human organism.
The prebiotics studied so far are various types of fiber found in plant-based foods. In concrete terms, it is Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) and galactooligosaccharides (GOS) as well as inulin.
But other substances that are present in various foods can also be very beneficial for our intestinal flora:
- Different types of fiber found in onions, leeks, asparagus, artichokes, seeds (chia and flax seeds), potatoes, carrots, and apples are also good prebiotics.
- The polyphenols in cocoa, red fruits and certain spices also have prebiotic effects.
- Olive oil, dried fruits, and oily fish also contain prebiotics.
What are probiotics?
You now know what prebiotics are. We are therefore moving on to explaining how probiotics work so that you can become even more aware of the differences. The term “probiotic” literally means “for life”.
The most recognized definition of probiotics was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). It stipulates the following:
So it is no longer about nourishment for the healthy intestinal bacteria, but about the living organisms themselves. Most probiotics are produced by the fermentation of food.
The best studied bacteria include the groups Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium . We can find these in certain foods or in supplements.
The main sources of probiotics
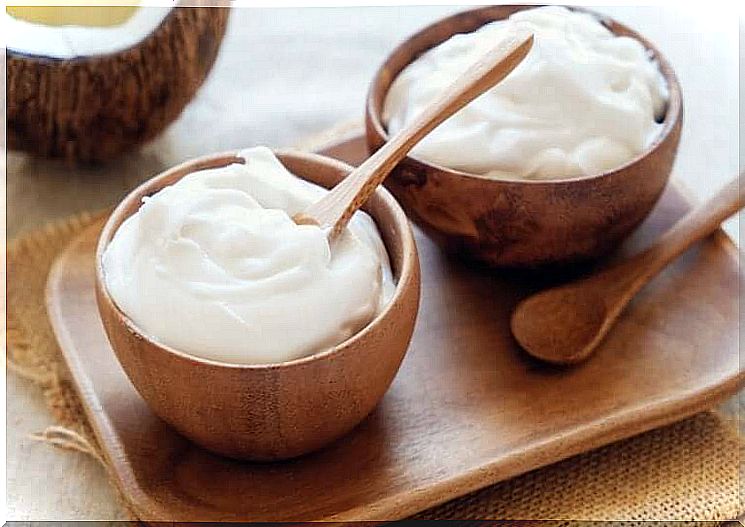

Yogurt is high in probiotics and easily available. Pure natural yoghurt, which provides lactobacilli and streptococci, is best . Kefir is also very healthy and provides other types of strains of bacteria.
Another important source of probiotics is fermented vegetables, such as sauerkraut, pickled vegetables, or pickles. In Asian gastronomy, miso (a paste made from fermented soy) and tempeh (fermented soybeans) should be mentioned.
This list should also include kombucha, a slightly tingling drink that is made through fermentation and has become very popular in recent years.
Prebiotics and Probiotics: Conclusion
The best way to differentiate between prebiotics and probiotics is to understand their different but complementary functions. Probiotics don’t make sense unless they’re properly nourished by prebiotics afterwards.
However, we must also consider the latest research, because the science and research in the field of prebiotics and probiotics continues to come up with new knowledge and discoveries.