What Is A Sarcoma Or Soft Tissue Tumor?
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor of the connective and supporting tissue that can develop aggressively. Find out in today’s article how this happens and what treatment options are available.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor of the connective and supporting tissue that spreads uncontrollably. The malignant tumor cells arise in the bones and soft tissues of the body. These include adipose tissue, muscles, cartilage and blood vessels. It is therefore also referred to as a soft tissue tumor.
Sarcomas are relatively rare. It is estimated that less than 1 percent of all malignant tumors are due to soft tissue sarcomas. Sarcomas cause 2 percent of cancer-related deaths.
This type of tumor can occur in any area of the body, but most often it manifests itself in the extremities, both in the legs and in the arms. They also occur in the stomach area or in the head.
Mostly people between 40 and 70 years are affected. However, some types of sarcoma also occur in children. In general, men are more likely to suffer from it than women.
Causes of Sarcoma
As with many cancers , the specific causes of tumor cell development cannot be determined. Experts assume that various factors occur at the same time and lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of malignant cells.
The exact risk factors for certain types of sarcoma could not be clearly defined until now. This makes preventive measures difficult. It is to be hoped that current scientific studies will find out more about soft tissue tumors and produce helpful results.
However, experience and science have identified a few risk factors:
- Genetic diseases: Certain genetic pathologies, such as neurofibromatosis, often lead to the development of a soft tissue tumor.
- Radiation therapy: People who are treated with radiation therapy to treat thyroid problems or neoplasms, for example, can also develop sarcoma.
- Viruses: Various viral infections increase the likelihood of developing a soft tissue tumor. For example, Kaposi’s sarcoma is associated with a specific type of herpes.
- Lymphedema: The accumulation of fluid in the soft tissues of the organism over a long period of time, i.e. if the problem is chronic, can also cause neoplasms in these tissues.
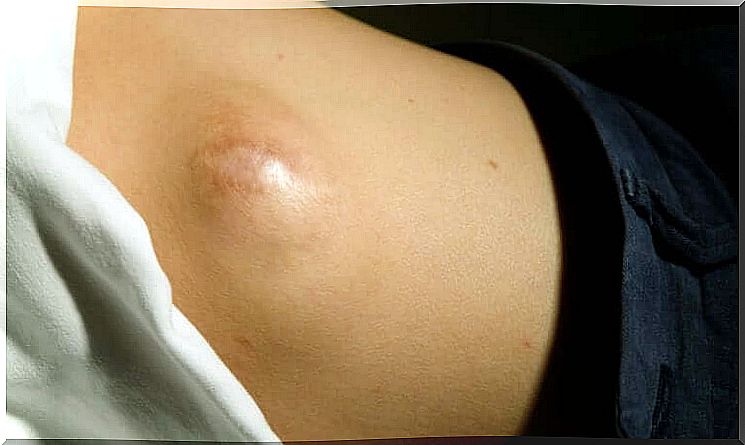
What are the symptoms of a sarcoma?
Soft tissue sarcoma is usually not painful unless it has progressed enough to put pressure on a part of the body. The diagnosis is therefore complicated and the suspicion that a sarcoma may be present usually arises relatively late.
One reason why there are few symptoms is that soft tissue tumors are often very deep. This often delays the diagnosis.
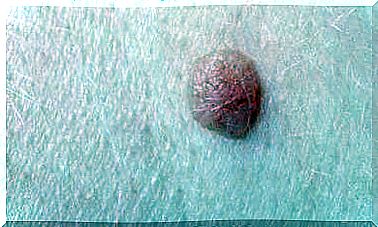
The appearance of a lump is one of the most common symptoms. If this is the case, you definitely need to see a doctor. Of course, there can be another disease, but a tumor must be examined.
Sarcoma: diagnosis and treatment
If the doctor suspects a soft tissue tumor, they will use imaging tests to make a diagnosis. An ultrasound examination, magnetic resonance or computed tomography are very helpful.
If these methods confirm the suspicion, a biopsy is required. This can be used to make the definitive diagnosis to confirm the presence of a sarcoma if necessary.
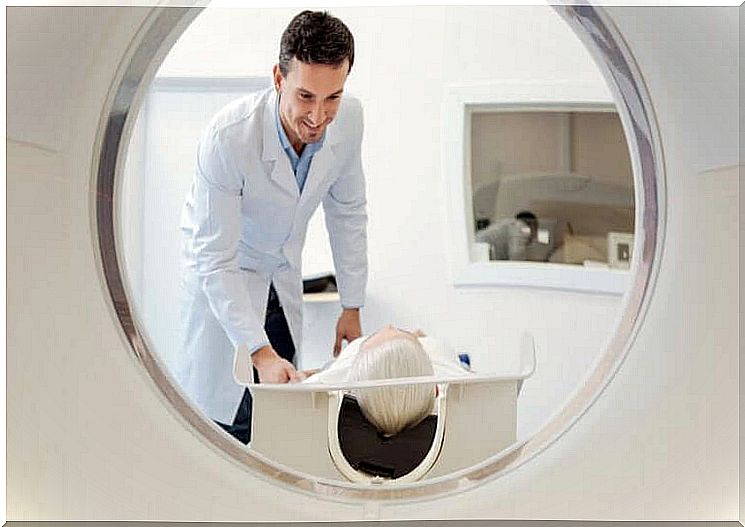

Once diagnosed with sarcoma, the following treatments are possible:
- Surgery: Often times, surgery can solve the problem without further treatment.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy can partly complement an operation. If the surgical resection does not remove all free edge injuries, radiation therapy may be necessary.
- Chemotherapy: A soft tissue tumor does not always require chemotherapy. However, if the tumor is bad or in a difficult location, chemotherapy may be necessary.
- Immunotherapy: This relatively new and promising treatment method uses biological drugs against cancer. This is to stop the process by which the malignant cells block the body’s immune response. However, these are expensive drugs that are not available everywhere.
Final remark
If a tumor occurs, a doctor’s visit is essential. The doctor will then conduct the necessary examinations to get to the bottom of the cause. It doesn’t have to be a serious problem, but it is important to be on your guard.
Because the later the diagnosis is made, the more difficult and slower the treatment. However, if a tumor is detected at an early stage, the corresponding therapies can be used efficiently.